This page allows you compare the features of the Intel Xeon Processor Scalable processors:
- 1st Gen Intel Xeon Scalable (formerly codenamed "Skylake", SKL)
- 2nd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Cascade Lake", CLX)
- 3rd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Cooper Lake" CPX and "Ice Lake" ICX)
- 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Sapphire Rapids" SPR)
- 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Emerald Rapids" EMR)
- Intel Xeon 6 ("Sierra Forest" SRF and "Granite Rapids" GNR)
Introduction
ThinkSystem servers incorporate Intel Xeon Scalable Family processors to enable critical business workloads and applications. The Intel scalable design provides significant improvement in performance, advanced reliability, scalability and hardware-enhanced security. Enhancements include higher per-core performance, greater memory bandwidth, expanded I/O, and improved security. This page allows you compare the features of the processors.
Mainstream field: Processors marked as Mainstream can be configured in DCSC (select Full Mode) or in x-config. For processors marked as Extended, please contact your Lenovo sales representative.
SPEC CPU results: The table includes SPEC CPU results. See the SPECcpu2017 results section below the table regarding the use of this data.
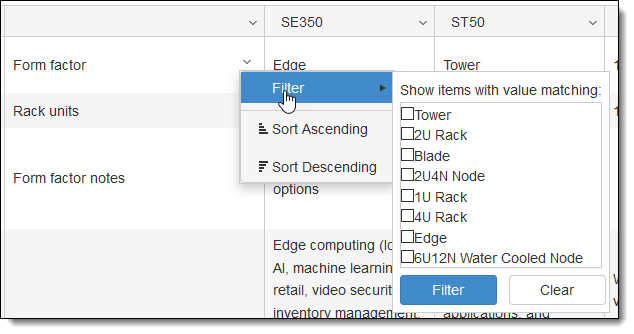
To search: Enter a search term and click Search, or click Add Filter to perform more advanced searching. For information on how to view, rearrange and export the data, click the Help link.
Additional information
Platforms and processors
Intel platforms and their associated processor families are as follows:
- Intel Purley platform
- 1st Gen Intel Xeon Scalable (formerly codenamed "Skylake", SKL)
- 2nd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Cascade Lake", CLX)
- Intel Whitley platform
- 3rd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Ice Lake" ICX)
- Intel Cedar Island platform
- 3rd Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Cooper Lake" CPX)
- Intel Eagle Stream (EGS) platform
- 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Sapphire Rapids" SPR)
- 5th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable ("Emerald Rapids" EMR)
- Intel Birch Stream (BHS) platform
- Intel Xeon 6 ("Sierra Forest" SRF and "Granite Rapids" GNR)
Processor suffixes
Some of the processors include a suffix letter in the processor model number to indicate an additional feature:
- Intel Xeon 6 processors use these suffixes:
- P: Processor contains Performance cores (P-cores)
- E: Processor contains Efficient cores (E-cores)
- 4th Gen and 5th Gen processors use these suffixes:
- +: Includes 1 of each of the four accelerators: DSA, IAA, QAT, DLB
- H: Database and Analytics workloads
- M: Media Transcode workloads
- N: Network/5G/Edge workloads (High TPT / Low Latency)
- P: Cloud and IaaS workloads
- Q: Liquid cooling
- S: Storage & HCI workloads
- T: Long-life Use/High Tcase
- U: 1-socket only (some workload-specific SKUs may also be 1-socket)
- V: Cloud and SaaS workloads
- Y: SST-PP enabled (some workload-specific SKUs may also support SST-PP)
- Y+: SST-PP enabled and includes 1 of each of the accelerators
- 3rd Gen processors use these suffixes:
- H: 4-Socket capable processor supporting up to 1.125TB memory per processor
- HL: 4-Socket capable processor supporting up to 4.5TB memory per processor
- M: Media Processing optimized
- N: NFV optimized
- P: High frequency-optimized for IaaS virtualization customers
- Q: Optimized for liquid cooling
- S: Large (512GB) SGX Enclave size
- T: High Tcase
- U: Single socket
- V: High density/low power-optimized for SaaS virtualization customers
- Y: Speed Select
- 1st Gen and 2nd Gen processors use these suffixes:
- F: Integrated Omni-Path Architecture (OPA) Fabric
- L: Large memory tier (supports total memory up to 4.5TB per processor)
- M: Medium memory tier (supports total memory up to 2TB per Gen 2 processor or 1.5TB per Gen 1 processor)
- N: NFV optimized
- S: Search optimized
- T: High Tcase
- U: Single socket
- V: VM Density optimized
- Y: Speed Select
Notes:
- Y suffix: Speed Select (Y suffix) processors support different core counts and corresponding core speeds.
- B suffix: B is not a feature suffix, but instead used by Intel to distinguish between the Xeon Gold 5218 and the Xeon Gold 5218B processors. These two processor models have the same core counts, frequencies, and features, however they are based on different die configurations. You should not install 5218 and 5218B processors in the same server
- R suffix: R is not a feature suffix, but instead is used to indicate the processor is one of the set of refreshed (R) second-generation processors that were announced February 2020.
SPECcpu2017 results
There are four rows in the table above that list SPEC CPU results, which have been extracted from the SPECcpu results page on spec.org. The results are from the following servers:
- 1st Gen processors: ThinkSystem SR650
- 2nd Gen processors: ThinkSystem SR650
- 3rd Gen processors (2-socket): ThinkSystem SR650 V2
- 3rd Gen processors (4-socket): ThinkSystem SR860 V2
- 4th Gen processors: ThinkSystem SR650 V3
- 5th Gen processors: ThinkSystem SR650 V3
- 6th Gen processors: ThinkSystem SR630 V4 and SC750 V4
- Max Series processors: ThinkSystem SD650 V3
The results provide a way to compare the integer and floating point performance of the processors:
- SPECspeed scores are useful for measuring single-threaded compute-intensive applications, such as High Frequency Trading (HFT) and other financial industry workloads.
- SPECrate scores are useful for measuring multi-threaded compute-intensive applications, such as High Performance Computing (HPC) workloads.
Note that these results were published over time and may use a different version of Intel C/C++ Compiler. New compiler versions can improve SPEC CPU scores by 5-10%. Take this into consideration when comparing processor models. You can determine the compiler versions used by reviewing the results on the SPEC results page.
For additional information, see these resources: